Focos
Analista de sistemas de información geográfica (analista SIG), administrador de sistemas de información geográfica (administrador SIG), analista de sistemas de información geográfica (analista SIG), coordinador de sistemas de información geográfica (coordinador SIG), técnico SIG (técnico de sistemas de información geográfica), analista de recursos, especialista en teledetección, científico de datos geoespaciales, arquitecto de soluciones geoespaciales, ingeniero geomático.
La superficie terrestre es un área de estudio fascinante, pero existen innumerables retos a la hora de recopilar y comprender los datos sobre ella. Por eso, los informáticos crearon los sistemas de información geográfica (SIG) para ayudar a capturar, examinar y mostrar datos procedentes de diversas fuentes. Desde cadenas montañosas hasta calles suburbanas, la información que proporcionan los programas SIG puede utilizarse para miles de aplicaciones. Pero se necesitan expertos cualificados, conocidos como especialistas en sistemas de información geográfica, para utilizar correctamente estos complejos sistemas informáticos.
Las funciones de los especialistas en SIG pueden incluir el diseño o desarrollo de sistemas y bases de datos SIG, que luego utilizan para ayudar a científicos e investigadores en diversos proyectos que requieren datos geoespaciales sobre determinadas ubicaciones. Al introducir datos en programas de cartografía, pueden crear y personalizar mapas que incorporan todo tipo de información. Las posibilidades son prácticamente infinitas, pero algunos ejemplos son: mapas que muestran estadísticas demográficas y democráticas, mapas que muestran hábitats de fauna silvestre y mapas que muestran características de terrenos de difícil acceso.
La tecnología SIG es utilizada por los gobiernos locales para obras públicas, planificación y gestión medioambiental, y registros de propiedad. También se utiliza en el sector inmobiliario, la seguridad pública, la defensa, el transporte, la gestión sanitaria, la extracción de recursos naturales y otros muchos campos. Muchos consideran Google Maps es un SIG que se conecta al GPS (sistema de posicionamiento global por satélite) para ofrecer servicios de navegación gratuitos.
- Ayudar a recopilar y utilizar datos geoespaciales con fines de planificación.
- Empoderando a miles de organizaciones con herramientas para mejorar sus operaciones.
- Proteger a los trabajadores humanos del trabajo y los riesgos del mapeo manual.
Horario de trabajo
- Los especialistas en sistemas de información geográfica suelen trabajar a tiempo completo. En algunos casos, es necesario realizar horas extras cuando un trabajo es urgente. Algunos pueden trabajar solo a tiempo parcial, según sea necesario.
Funciones típicas
- Discutir el alcance del proyecto, las expectativas, los presupuestos, los plazos y las responsabilidades.
- Manténgase informado sobre una amplia gama de tipos de proyectos, incluidos los relacionados con ingeniería civil, ingeniería eléctrica, topografía, energía solar y eólica, y desarrollo de terrenos para uso residencial y comercial.
- Métodos de investigación y lugares desde los que recopilar datos
- Recopilar y evaluar datos de diversas fuentes aprobadas, como sensores remotos.
- Enlace con el personal de apoyo sobre el terreno, según sea necesario.
- Diseñar y ayudar a construir sistemas informáticos integrados, bases de datos, programas de modelización y modelos científicos/matemáticos.
- Modificar las bases de datos de los Sistemas de Información Geográfica existentes, según sea necesario.
- Programar en GIS, realizar pruebas funcionales y solucionar errores.
- Sugerir mejoras, actualizaciones y otros cambios en el SIG.
- Mantener la documentación técnica de los procesos de trabajo.
- Preparar e introducir datos en bases de datos. Evaluar los datos existentes ya cargados.
- Realizar análisis de datos y tomar nota de las tendencias y patrones.
- Realizar modelización y análisis geoespaciales.
- Revisar fotos aéreas y ortofotos.
- Decidir los elementos cartográficos adecuados que se utilizarán en los informes.
- Utilice el SIG para preparar informes, gráficos, tablas, capas de datos, representaciones 3D
, mapas, etc. - Interpretar los resultados para los clientes o las partes interesadas.
- Colaborar con el personal o los equipos pertinentes; debatir los resultados.
Responsabilidades adicionales
- Investigar formas para que los SIG funcionen con el software de los sistemas de posicionamiento global.
- Trabajar en aplicaciones móviles GIS
- Garantizar el control de calidad y la precisión de los datos.
- Ofrecer formación y asistencia técnica a los usuarios.
- Manténgase al día sobre los cambios en la industria y los avances tecnológicos.
- Asista a eventos de organizaciones profesionales para compartir información y aprender de los demás.
Habilidades sociales
- Coordinación de actividades
- Analítico
- Atención al detalle
- Colaboración
- Pensamiento crítico
- Razonamiento deductivo e inductivo
- Orientado a los detalles
- Imparcial
- Independiente
- Supervisión
- Visión normal del color
- Objetivo
- Organizado
- Paciente
- Perceptivo
- Resolución de problemas
- Comprensión lectora
- Fuertes habilidades de comunicación
- Gestión del tiempo
- Visualización
Habilidades técnicas
- Principios y procedimientos básicos de ingeniería
- Programas de diseño asistido por ordenador (CAD)
- Software de análisis de datos
- Sistemas de gestión de bases de datos
- Software de diseño, planos, modelos 3D, planos técnicos.
- Software de entorno de desarrollo
- Planificación de recursos empresariales
- Sistemas de información geográfica, como ESRI ArcGIS.
- Lenguajes de programación de la industria geoespacial, incluyendo Python, JavaScript, C+, HTML/CSS, Swift, Java, C#, SQL, PHP, Rust, Lotlin, Ruby, TypeScript, Matlad, Go, etc.
- Google Earth, archivos KMZ y lidar
- Programas de gráficos/imágenes fotográficas
- Software de creación de mapas como Manifold System de CDA International o ITT Visual Information Solutions.
- Software de servicios móviles basados en la localización
- Experiencia previa en/familiaridad con ingenieros consultores y/o topógrafos.
- Software científico, como Coordinate Geometry COGO
Conocimientos de geografía
- Bancos
- Agencias municipales, estatales y federales
- Empresas de ingeniería civil
- Empresas comerciales y fábricas
- Proveedores de instalación de sistemas de comunicaciones
- Instituciones educativas y de investigación
- Agencias de ciencias medioambientales
- Instaladores de sistemas de alarma contra incendios/seguridad
- Servicios forestales
- Agencias de servicios sanitarios y sociales
- Instaladores de sistemas de climatización
- Compañías de seguros
- Organismos encargados de hacer cumplir la ley
- Grupos de ciencias políticas
- Agencias inmobiliarias
- Negocios minoristas
- Empresas de gestión de la cadena de suministro
- Urbanistas
- Proveedores de servicios públicos
La tecnología GIS se utiliza, o puede utilizarse, en prácticamente todos los sectores imaginables. Para hacerse una idea de lo dependientes que nos hemos vuelto de estos sistemas críticos, consulte el artículo de Nobel «20 formas en que se utilizan los datos GIS en los negocios y en la vida cotidiana». El GIS es un activo fundamental que se utiliza para tomar decisiones importantes que afectan a todo, desde los beneficios de las empresas hasta la seguridad pública. Debido a nuestra dependencia del GIS, los datos y resultados generados por este sistema deben ser lo más precisos posible.
Los especialistas en SIG son fundamentales para garantizar que los sistemas funcionen según lo previsto y proporcionen resultados fiables. En Stack Exchange se señaló un ejemplo antiguo de un error en un SIG, en el que se observaba cómo el uso incorrecto de los aspectos espaciales tergiversaba por completo el «alcance potencial de los misiles de Corea del Norte». Un simple descuido llevó a The Economist a informar de una enorme subestimación del verdadero alcance de una posible amenaza militar.
El campo de los SIG nació a principios de la década de 1960 y se ha desarrollado sin cesar desde entonces. Las tendencias actuales incluyen el uso cada vez mayor del análisis 3D para añadir valor a los proyectos. Otra área que está experimentando cambios interesantes es la de los SIG web, que llevan la potencia de estos sistemas a comunidades mucho más amplias. Esto, a su vez, está ampliando las oportunidades, atrayendo a más personas a aprender habilidades SIG y contribuyendo al avance.
Además, la integración del SIG con el modelado de información de edificios y el diseño y dibujo asistido por ordenador está transformando y ampliando las capacidades de estos sistemas. Por supuesto, al igual que en muchos otros campos, la inteligencia artificial y el aprendizaje automático han entrado en escena para aprovechar todo el potencial del SIG, al tiempo que se aprovechan los datos en tiempo real y los «macrodatos».
Cada una de las tendencias anteriores es tan amplia que ningún especialista en SIG puede estudiarlas todas, pero es recomendable estar familiarizado con todos los cambios e innovaciones que se están produciendo.
Es probable que a los especialistas en sistemas de información geográfica les gustara trabajar con ordenadores desde una edad temprana. Quizás se interesaran por cómo funcionan las cosas o por los datos, las estadísticas, las cifras e incluso las curiosidades. También es posible que disfrutaran utilizando software para crear arte o diseños gráficos. Es posible que los futuros especialistas tuvieran un gran interés en algún campo concreto, como los estudios medioambientales, que querían mejorar con el uso de la tecnología SIG.
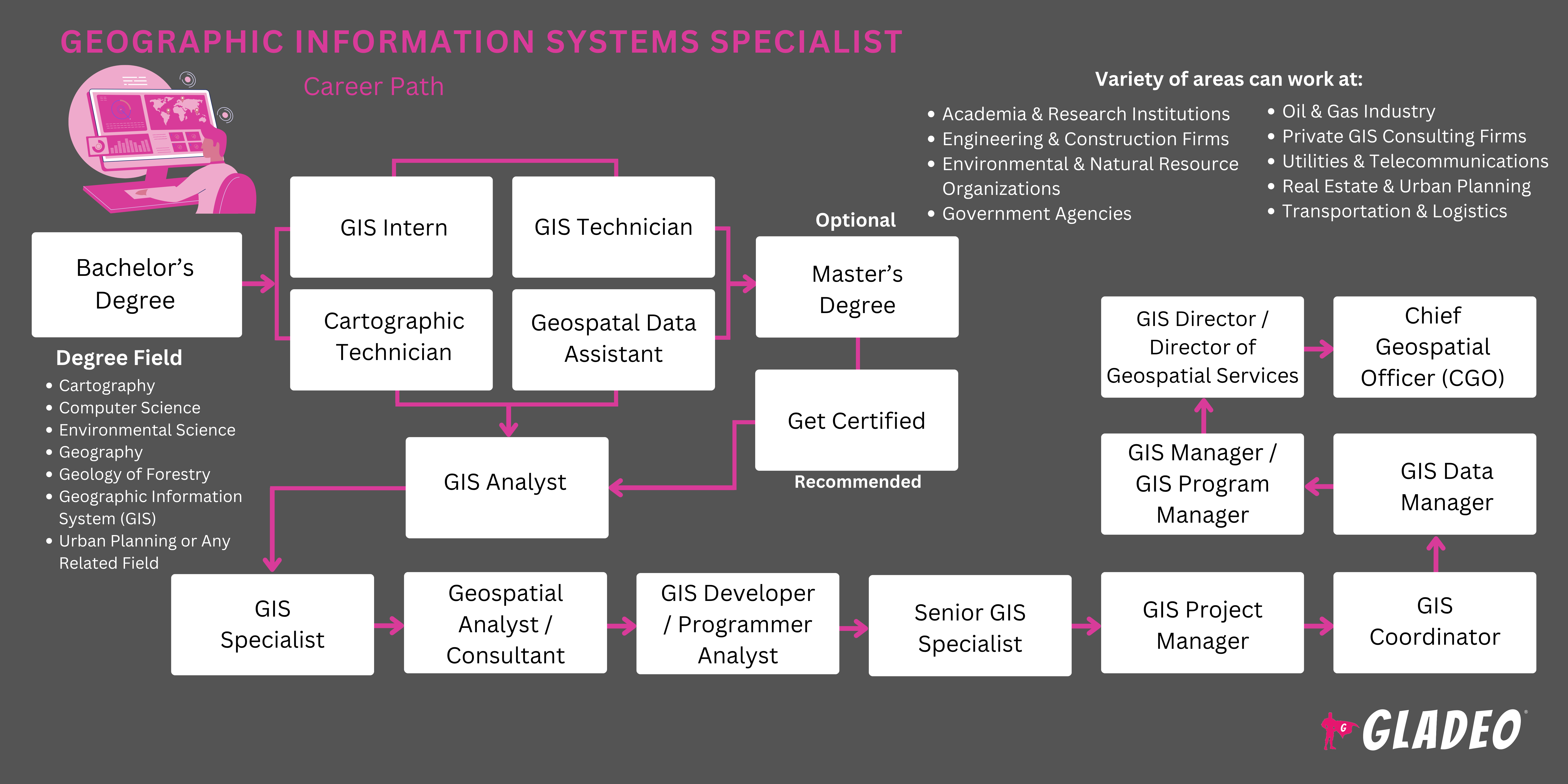
- Los especialistas en SIG deben tener como mínimo una licenciatura en SIG, geografía o estudios medioambientales.
- Se pueden considerar otras especialidades relacionadas si el estudiante tiene suficiente experiencia relevante en SIG.
- Los estudiantes deberán aprender a utilizar diversos programas de software, como la suite Esri ArcGIS Desktop, para realizar análisis avanzados, 2D y 3D, procesamiento de imágenes, visualización avanzada, conexión y uso compartido, y gestión de datos.
- Otros temas de aprendizaje incluyen:
- Archivos AutoCAD y DWG
- Métodos, teorías y principios cartográficos
- Geometría coordinada COGO
- Sistemas de coordenadas
- Bases de datos geográficos
- Lenguajes de programación GIS como Python, JavaScript, C+, HTML/CSS, Swift, Java, etc.
- Google Earth y archivos KMZ
- Recopilación y gestión de datos GPS
- Conjuntos de datos LiDAR
- Software de creación de mapas como Manifold System de CDA International o ITT Visual Information Solutions.
- Archivos Shapefile
- Conjuntos de datos vectoriales y rasterizados
- Existen varias certificaciones nacionales disponibles para especialistas en SIG, entre las que se incluyen:
- Adobe Systems Incorporated - Certificación de experto en prácticas empresariales de Adobe Campaign Classic
- Sociedad Americana de Fotogrametría y Teledetección - Sociedad de Imágenes e Información Geoespacial -
- Técnico certificado en SIG/SIL
- Científico certificado en cartografía - UAS
- Científico certificado en cartografía Lidar
- Técnico certificado en sistemas aéreos no tripulados (UAS)
3. Instituto de Investigación de Sistemas Ambientales -
- API de ArcGIS para JavaScript
- Asociado de ArcGIS Desktop 10.5
- ArcGIS Desktop Entry 10.5
- ArcGIS Desktop Professional 10.5
- Asociado en Administración Empresarial 10.5
- Gestión de datos geográficos empresariales - Asociado 10.5
- Gestión de datos geográficos empresariales - Professional 10.5
- Asociado de diseño de sistemas empresariales 10.5
4. Instituto de Certificación SIG - Profesional en Sistemas de Información Geográfica
5. Agencia Nacional de Inteligencia Geoespacial -
- Certificación profesional en ciencias aplicadas
- Fundamentos de la certificación profesional
- Certificación profesional en recopilación de información geoespacial (GEOINT)
- Certificación profesional en análisis geoespacial
- Certificación profesional en gestión de datos geoespaciales
- Certificación profesional en Geografía Humana
- Certificación profesional en análisis de imágenes
- Certificación profesional marítima
6. Fundación de Inteligencia Geoespacial de los Estados Unidos -
- Profesional certificado en GEOINT: SIG y herramientas de análisis.
- Profesional certificado en GEOINT: teledetección y análisis de imágenes.
- Profesional certificado en GEOINT - Gestión de datos geoespaciales
7. WorldatWork - Profesional certificado en prestaciones sociales
- Ten en cuenta el costo de la matrícula, los descuentos y las oportunidades de becas locales (además de la ayuda federal).
- Piensa en tu horario y flexibilidad a la hora de decidir si matricularte en un programa presencial, online o híbrido.
- Echa un vistazo a los premios y logros del profesorado del programa para ver en qué han trabajado.
- Observe detenidamente las instalaciones en las que imparten clases y el equipo y software con el que permiten a los alumnos formarse.
- Revisa las estadísticas de inserción laboral y los detalles sobre la red de antiguos alumnos del programa.
- Los cursos de secundaria como informática, programación informática, geografía y economía pueden ayudar a preparar a los estudiantes para un programa universitario de SIG.
- Considera solicitar un puesto de aprendiz relacionado con los SIG.
- Si puedes, intenta adquirir experiencia laboral mediante trabajos a tiempo parcial que te permitan desarrollar habilidades y practicar.
- Anota los nombres y la información de contacto de las personas con las que trabajas, ya que algún día podrían servirte como referencias laborales.
- Estudia libros, artículos y tutoriales en vídeo relacionados con las numerosas aplicaciones de la tecnología SIG. Intenta determinar en qué área quieres trabajar después de graduarte.
- Pregunte a algunos especialistas en SIG con experiencia si puede acompañarlos para hacerse una idea de sus actividades diarias.
- Únase a organizaciones profesionales como la Agencia Nacional de Inteligencia Geoespacial para conocer las tendencias y ampliar su red de contactos.
- Obtenga una certificación en un área especializada para reforzar sus credenciales.
- Participa como voluntario en actividades escolares en las que puedas aprender a trabajar eficazmente en equipo, practicar tus habilidades sociales y gestionar proyectos.
- No esperes para empezar a redactar tu currículum. Lleva un registro del software y los equipos que has aprendido a utilizar, para no perder la pista.
- Revisa los criterios de los puestos de trabajo con antelación consultando las ofertas publicadas en Indeed y otros portales de empleo.
- Los programas de formación profesional relacionados con los SIG pueden ser una buena forma de introducirse en este sector laboral.
- Acumula toda la experiencia que puedas antes de presentar tu solicitud.
- Configura alertas en portales de empleo como Indeed, Simply Hired, Glassdoor y Zippia.
- Lea atentamente los anuncios para asegurarse de que cumple todos los requisitos para presentar su solicitud.
- Ponte en contacto con especialistas en SIG en activo para preguntarles cómo consiguieron sus puestos de trabajo.
- Informa a tu red de contactos de que has comenzado tu búsqueda de empleo para que puedan avisarte de las vacantes disponibles.
- Pide ayuda al programa o centro de orientación profesional de tu universidad para buscar trabajo.
- Muchos programas sirven como conductos para los reclutadores, ¡así que hazles saber que estás listo para trabajar!
- Revisa las plantillas de currículum de especialista en SIG para obtener ideas sobre la redacción y los formatos.
- Enumera toda tu formación académica, habilidades, capacitación y experiencia laboral en tu currículum, y pide a un amigo o editor que lo revise.
- Pregunte a sus antiguos profesores y supervisores si estarían dispuestos a servir como referencias personales.
- ¡Estudia las preguntas de la entrevista para especialistas en SIG y prepárate para las entrevistas!
- Entra en Quora y empieza a hacer preguntas sobre consejos laborales.
- ¡Vístete siempre de forma adecuada para tener éxito en las entrevistas de trabajo!
- Manténgase a la vanguardia mejorando constantemente sus habilidades y aprendiendo cosas nuevas a través de cursos en línea, como el curso «Gestión ágil de un SIG moderno» de Bootcamp GIS.
- Obtenga un máster o certificaciones avanzadas que le cualifiquen para puestos de mayor autoridad.
- Hablar con compañeros sobre los nuevos avances y usos del SIG.
- Demuestre liderazgo intelectual y ayude a su empleador a sacar el máximo partido a su SIG.
- Aprende a comunicar eficazmente los beneficios que aportas.
- Genere confianza siendo responsable, cumpliendo con los plazos y garantizando resultados precisos y de alta calidad.
- Investiga con diligencia para recopilar datos de fuentes fiables.
- Trata a todos con respeto y construye tu reputación como profesional íntegro.
- Sea transparente sobre las capacidades y ofrezca soluciones viables.
- Observe y aprenda de especialistas en SIG con más experiencia. Haga preguntas y tome notas sobre las mejores prácticas.
- Amplíe su red profesional en la comunidad y mediante una mayor participación en organizaciones profesionales.
- Intenta ganar premios y reconocimientos que queden bien en tu currículum.
- Mantén conversaciones francas con tu supervisor. Si tu empresa no ofrece oportunidades de ascenso, plantéate si quieres quedarte o cambiar de trabajo.
Sitios web
- Adobe Systems Incorporated
- Asociación Americana de Geógrafos
- Sociedad Americana de Fotogrametría y Teledetección - Sociedad de Imágenes e Información Geoespacial
- Sociedad Americana de Fotogrametría y Teledetección
- Instituto de Investigación de Sistemas Ambientales
- Asociación de Información y Tecnología Geoespacial
- Instituto de Certificación GIS
- Agencia Nacional de Inteligencia Geoespacial
- Consejo Nacional de Información Geográfica de los Estados
- Fundación de Inteligencia Geoespacial de los Estados Unidos
- URISA
- WorldatWork
Libros
- Introducción al SIG, segunda edición: conceptos fundamentales de geografía y cartografía, por Francis Harvey
- GIS para principiantes, de Michael N. DeMers
- Imágenes y SIG: mejores prácticas para extraer información de imágenes, por Kass Green, Russell Congalton, et al.
- Aprendizaje del análisis geoespacial con Python: Comprender los fundamentos del SIG y realizar análisis de datos de teledetección utilizando Python 3.7, por Joel Lawhead
¡O*Net enumera las siguientes ocupaciones relacionadas para tener en cuenta!
- Cartógrafos y fotogrametristas
- Científicos de datos
- Topógrafos geodésicos
- Desarrolladores de software
- Técnicos en topografía y cartografía
Fuente de noticias
Empleos destacados

Cursos y herramientas en línea

Expectativas salariales anuales
Los nuevos trabajadores comienzan con un salario de alrededor de 99 000 dólares. El salario medio es de 116 000 dólares al año. Los trabajadores con mucha experiencia pueden ganar alrededor de 150 000 dólares.
Expectativas salariales anuales
Los nuevos trabajadores comienzan con un salario de alrededor de 93 000 dólares. El salario medio es de 123 000 dólares al año. Los trabajadores con mucha experiencia pueden ganar alrededor de 139 000 dólares.
Expectativas salariales anuales
Los nuevos trabajadores comienzan con un salario de alrededor de 85 000 dólares. El salario medio es de 99 000 dólares al año. Los trabajadores con mucha experiencia pueden ganar alrededor de 130 000 dólares.








